EasyPoi官网
一、简单模版导出常用命令
- 空格分割
- 三目运算 {{test ? obj:obj2}}
- n: 表示 这个cell是数值类型 {{n:}}
- le: 代表长度{{le:()}} 在if/else 运用{{le:() > 8 ? obj1 : obj2}}
- fd: 格式化时间 {{fd:(obj;yyyy-MM-dd)}}
- fn: 格式化数字 {{fn:(obj;###.00)}}
- fe: 遍历数据,创建row
- !fe: 遍历数据不创建row
- $fe: 下移插入,把当前行,下面的行全部下移.size()行,然后插入
- #fe: 横向遍历
- v_fe: 横向遍历值
- !if: 删除当前列 {{!if:(test)}}
- 单引号表示常量值 ‘’ 比如’1’ 那么输出的就是 1
- &NULL& 空格
- &INDEX& 表示循环中的序号,自动添加
- ]] 换行符 多行遍历导出
- sum: 统计数据
- cal: 基础的+-X% 计算
- dict: 字典
- i18n: 国际化
常用命令
Excel循环
{{$fe:maplist t.province}} 二、最简单的导入
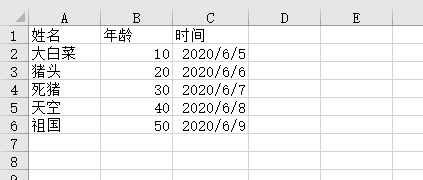
先看我们导入的Excel长什么样子
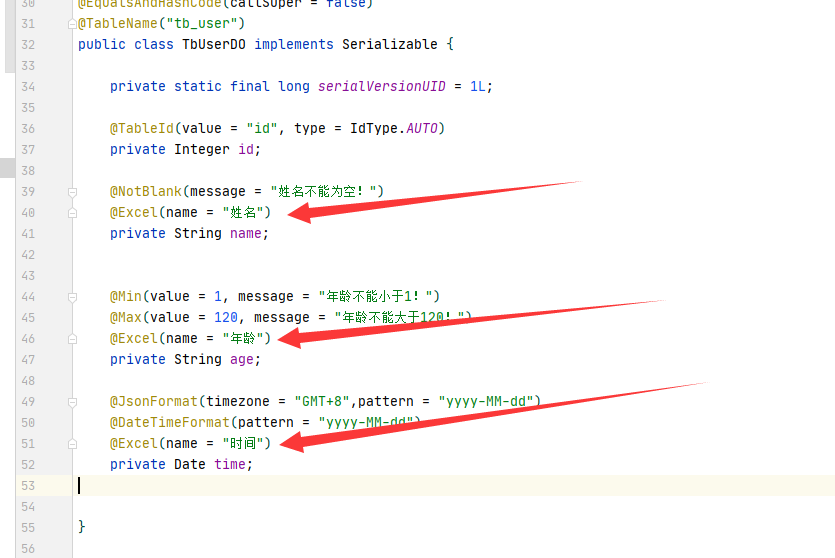
需要导入的字段加上相应的注解
上代码
@PostMapping("testFile")
public JsonData testFile(MultipartFile file) throws Exception {
ImportParams importParams = new ImportParams();
importParams.setStartRows(0);
List<TbUserDO> tbUserDOS = ExcelImportUtil.importExcel(file.getInputStream(), TbUserDO.class, importParams);
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
tbUserDOS.forEach(obj -> {
list.add(DateUtil.format(obj.getTime(), "yyyy/MM/dd"));
});
HashMap map = new HashMap();
map.put("tbUserDOS",tbUserDOS);
// 为了方便看导出时间是否准确
map.put("time",list);
return JsonData.buildSuccess(map);
} 返回JSON
点击查看完整内容
{
"code": 0,
"data": {
"tbUserDOS": [
{
"id": null,
"name": "大白菜",
"age": "10",
"time": "2020-06-05"
},
{
"id": null,
"name": "猪头",
"age": "20",
"time": "2020-06-06"
},
{
"id": null,
"name": "死猪",
"age": "30",
"time": "2020-06-07"
},
{
"id": null,
"name": "天空",
"age": "40",
"time": "2020-06-08"
},
{
"id": null,
"name": "祖国",
"age": "50",
"time": "2020-06-09"
}
],
"time": [
"2020/06/05",
"2020/06/06",
"2020/06/07",
"2020/06/08",
"2020/06/09"
]
},
"msg": "成功"
} 三、导入复杂表头操作
看看我们导入的是什么东西
实体类
package com.example.test05.demo.model;
import cn.afterturn.easypoi.excel.annotation.Excel;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* @author DBC
* @date 2022/8/1 15:40
* @network dbc655.top
*/
@Data
public class TestImport {
@Excel(name = "aa",fixedIndex = 0)
private String a;
@Excel(name = "a",fixedIndex = 1)
private String b;
@Excel(name = "b",fixedIndex = 2)
private String c;
@Excel(name = "c",fixedIndex = 3)
private String d;
@Excel(name = "d",fixedIndex = 4)
private String e;
@Excel(name = "e",fixedIndex = 5)
private String f;
@Excel(name = "f",fixedIndex = 6)
private String g;
@Excel(name = "a",fixedIndex = 7)
private String h;
@Excel(name = "b",fixedIndex = 8)
private String i;
@Excel(name = "c",fixedIndex = 9)
private String j;
@Excel(name = "d",fixedIndex = 10)
private String k;
}
简单的控制层
点击查看完整内容
package com.example.test05.demo.controller;
import cn.afterturn.easypoi.excel.ExcelImportUtil;
import cn.afterturn.easypoi.excel.entity.ImportParams;
import cn.afterturn.easypoi.excel.entity.result.ExcelImportResult;
import cn.hutool.core.io.FileUtil;
import com.example.test05.demo.model.TestImport;
import com.example.test05.demo.tool.JsonData;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author DBC
* @date 2022/8/1 15:39
* @network dbc655.top
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/import")
@Slf4j
public class ImportController {
/**
* 默认地址
*/
private static String importCachePath = "D:\\import\\";
@GetMapping("importExcel")
public JsonData importExcel(@RequestBody @NotNull MultipartFile multipartFile) throws Exception {
log.info("现在准备导入");
String fileName = "大法师";
int lastIndexOf = multipartFile.getOriginalFilename().lastIndexOf(".");
if (lastIndexOf >= 0) {
fileName += multipartFile.getOriginalFilename().substring(lastIndexOf);
}
File file = new File(importCachePath + fileName);
if (!file.getParentFile().exists()) {
file.mkdirs();
}
ImportParams params = new ImportParams();
params.setTitleRows(5);
params.setTitleRows(3);
// params.setConcurrentTask(true);
ExcelImportResult<TestImport> importResult =
ExcelImportUtil.importExcelMore(new FileInputStream(file), TestImport.class, params);
List list = importResult.getList();
log.info("现在导入的数据为:{}", list);
return JsonData.buildSuccess(list);
}
}
输出结果
{
"code": 0,
"data": [
{
"a": "大白菜",
"b": "白菜a1",
"c": "白菜b1",
"d": "白菜c1",
"e": "白菜d1",
"f": "白菜e1",
"g": "白菜f1",
"h": "白菜a2",
"i": "白菜b2",
"j": "白菜c2",
"k": "白菜d2"
},
{
"a": "小猪头",
"b": "猪头a1",
"c": "猪头b1",
"d": "猪头c1",
"e": "猪头d1",
"f": "猪头e1",
"g": "猪头f1",
"h": "猪头a2",
"i": "猪头b2",
"j": "猪头c2",
"k": "猪头d2"
}
],
"msg": "成功"
} 四、横向遍历导出表
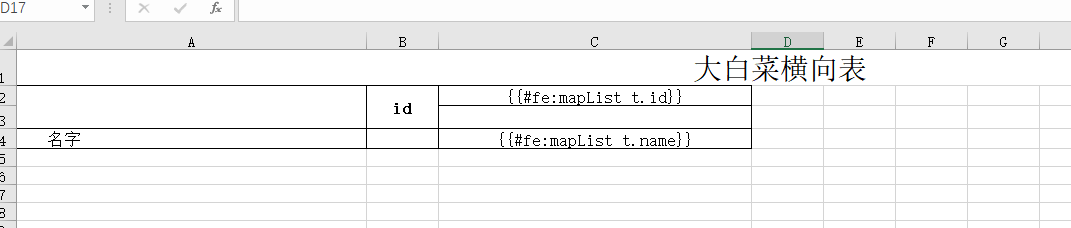
先看我们的Excel长什么样
具体代码
@GetMapping
public void test() throws IOException {
String fileName =
"大白菜横向统计表" + ".xlsx";
String templateFileName = "template/横向遍历.xlsx";
List<UserDO> userDOS = userService.list();
Map<String, Object> templateMapList = new HashMap<>();
templateMapList.put("mapList", userDOS);
TemplateExportParams template = new TemplateExportParams(templateFileName);
// 横向遍历
template.setColForEach(true);
Workbook workbook = ExcelExportUtil.exportExcel(template, templateMapList);
File savefile = new File("D:/excel/");
if (!savefile.exists()) {
savefile.mkdirs();
}
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/excel/横向遍历.xlsx");
workbook.write(fos);
fos.close();
}
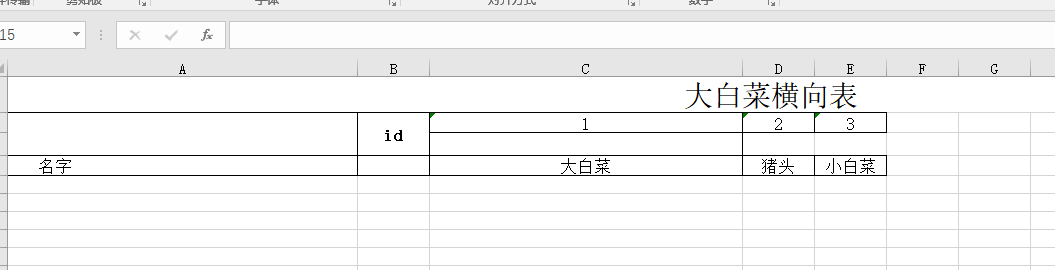
导出效果如下
本文作者为DBC,转载请注明。