一、我们先来看力扣的第203题
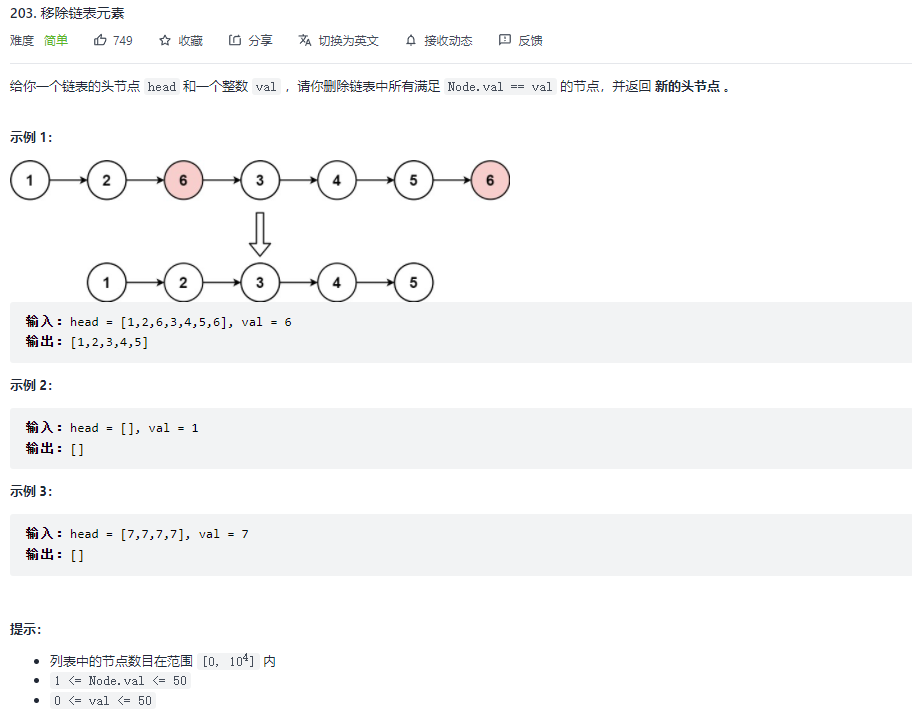
203. 移除链表元素
[aru_47] 点我前往具体题目
第一种:不使用虚拟头结点
public class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
while (head != null && head.val == val) {
ListNode delNode = head;
head = head.next;
delNode.next = null;
}
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode prev = head;
while (prev.next != null) {
if (prev.next.val == val) {
// ListNode delNode = prev.next;
// prev.next = delNode.next;
// delNode.next = null;
prev.next = prev.next.next;
} else {
prev = prev.next;
}
}
return head;
}
} 第二种:使用虚拟头结点
public class Solution2 {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode prev = dummyHead;
while (prev.next != null) {
if (prev.next.val == val) {
prev.next = prev.next.next;
} else {
prev = prev.next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
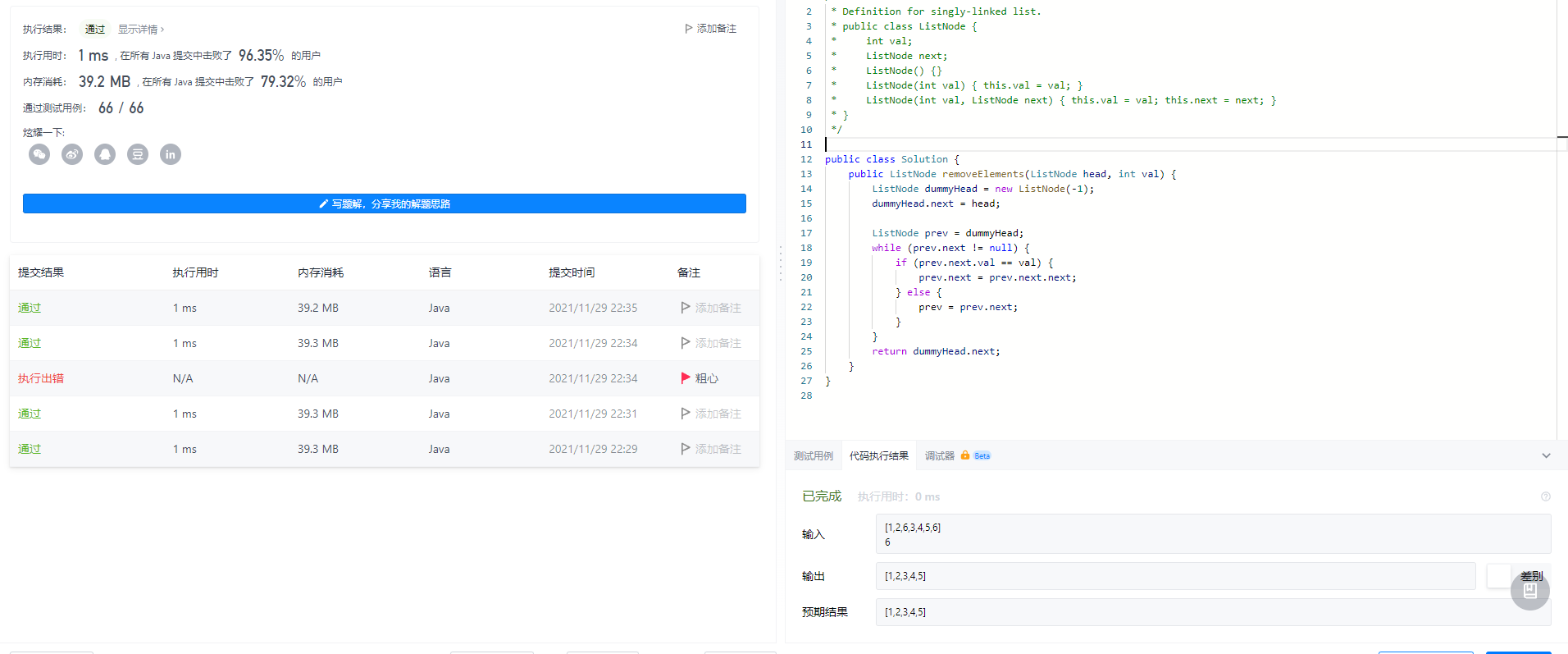
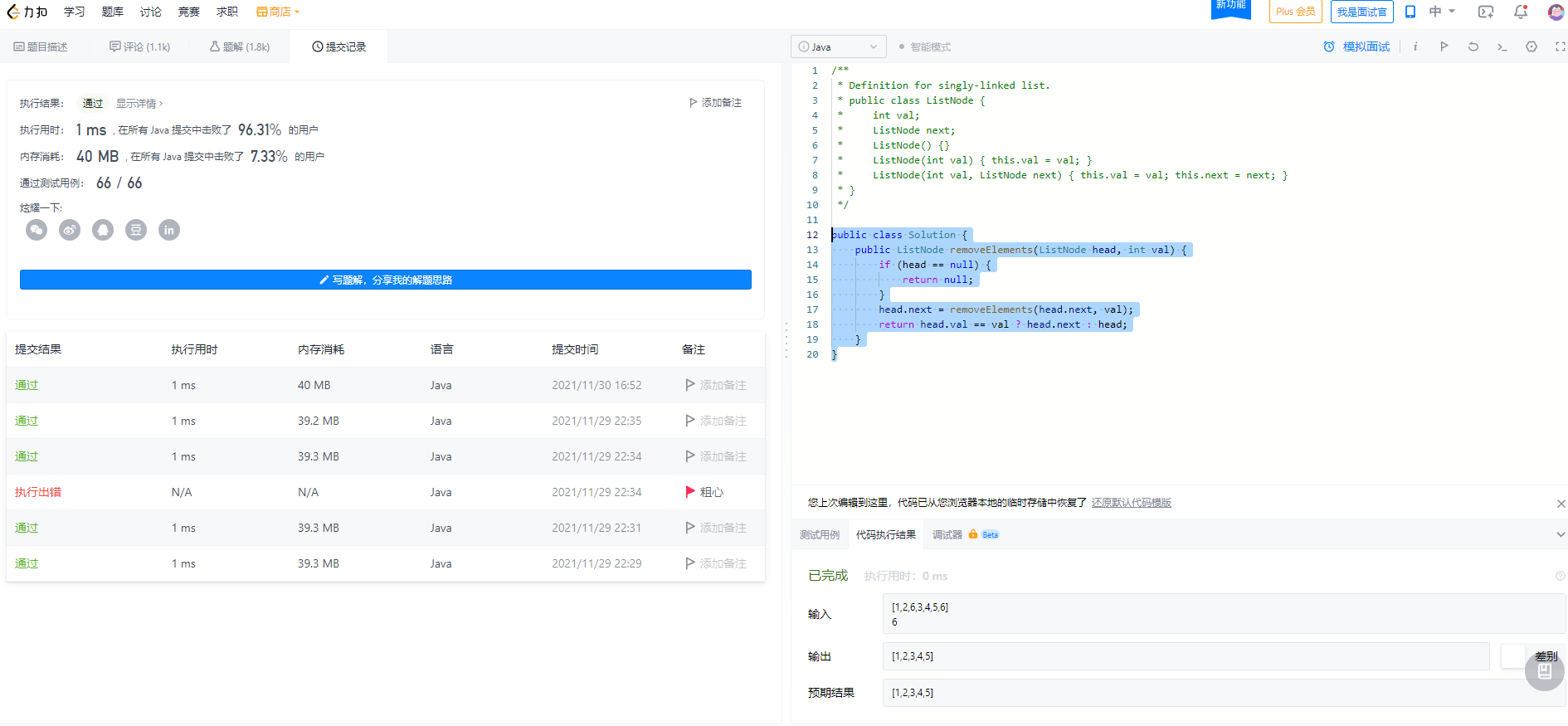
力扣提交情况——第二种提交
二、不用力扣测试,自己编写代码测试一下我们自己的链表
ListNode
点击查看完整内容
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
// 链表节点的构造函数
// 使用arr为参数,创建一个链表,当前的ListNode为链表头结点
ListNode(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("arr can not be empty");
}
this.val = arr[0];
ListNode cur = this;
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
cur.next = new ListNode(arr[i]);
cur = cur.next;
}
}
// 以当前节点为头结点的链表信息字符串
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
ListNode cur = this;
while (cur != null) {
res.append(cur.val + "->");
cur = cur.next;
}
res.append("NULL");
return res.toString();
}
} main方法测试一下
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1,2,3,5,6,7,8,5,6};
ListNode head = new ListNode(nums);
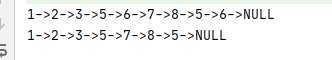
System.out.println(head);
ListNode res = new Solution2().removeElements(head,6);
System.out.println(res);
} 输出结果
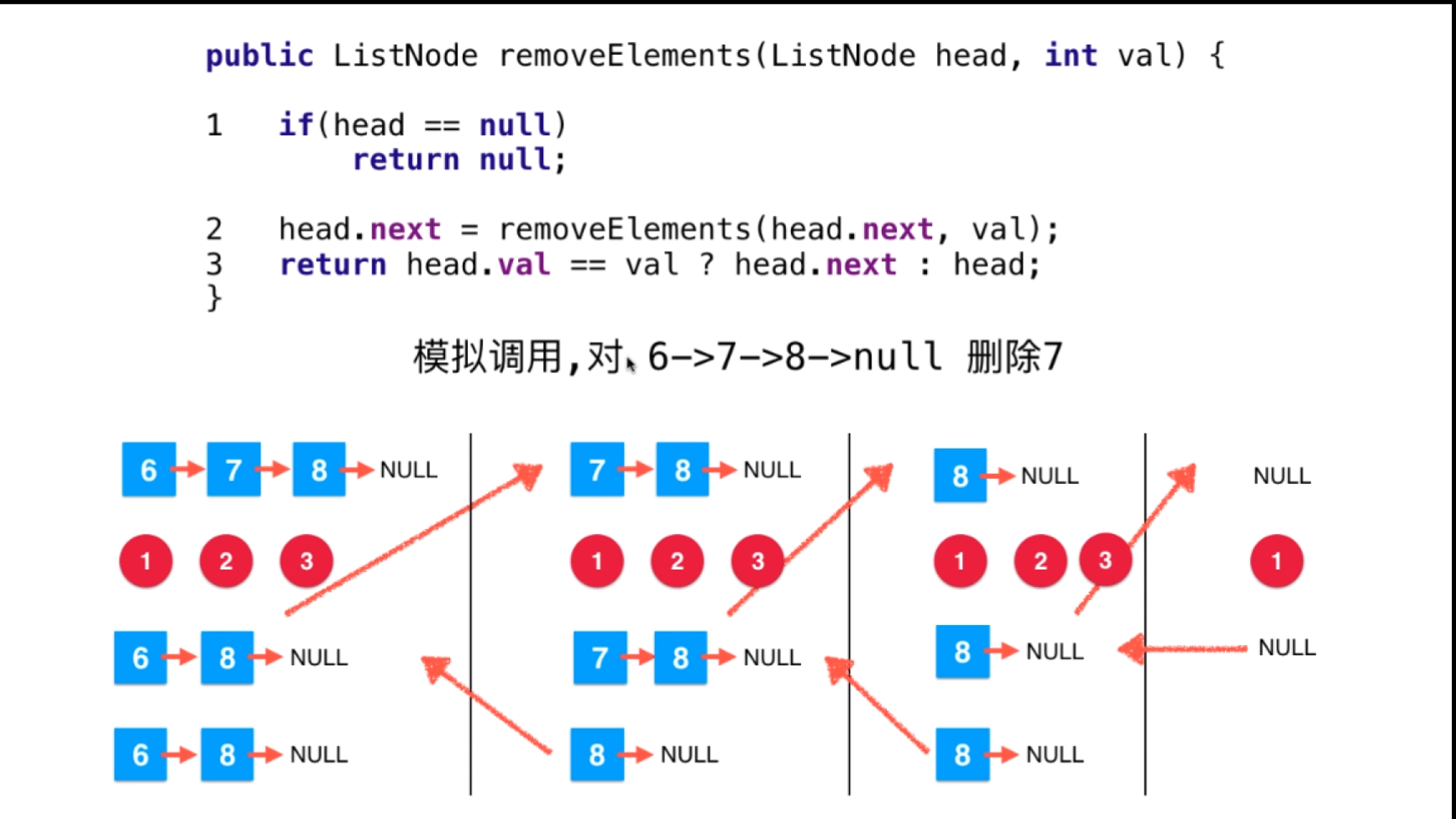
三、我们再来看一种递归的解决方案
public class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
head.next = removeElements(head.next, val);
return head.val == val ? head.next : head;
}
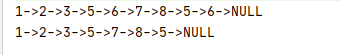
} 运行情况和提交力扣情况
四、递归函数的“微观”解读
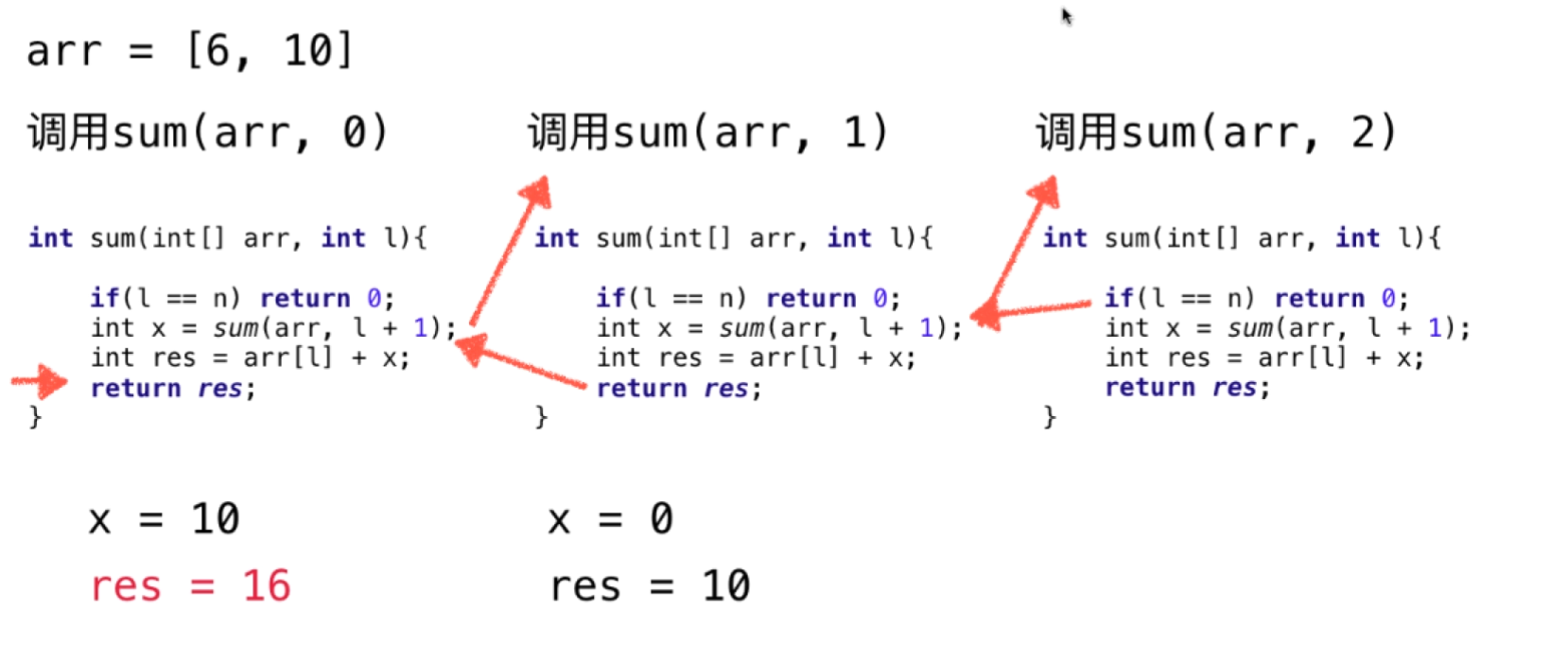
我们来看一个简单的例子来更好的理解递归思想
我们需要使用递归的方式来统计一下这个数组值的和
arr = [6,10]
我们来看一看这个代码,这就是一种递归的思想
public static int sum(int[] arr, int l) {
if (l == arr.length) {
return 0;
}
int x = sum(arr, l + 1);
int res = arr[l] + x;
return res;
} 这里我们用一张图来展示,引用全网最屌算法教程(个人认为)慕课网算法名师Liuyubobobo的图片来更好的说明这个例子
我们来看一个叫复杂的例子来更好的理解递归思想
总结
- 递归调用是有代价的:函数调用+系统栈控件
- 程序调用的系统栈
五、递归算法的调试
点击查看完整内容
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val, int depth) {
String depthString = generateDepthString(depth);
System.out.print(depthString);
System.out.println("Call: remove " + val + " in " + head);
if (head == null) {
System.out.print(depthString);
System.out.print("Return: " + head);
return head;
}
ListNode res = removeElements(head.next, val, depth + 1);
System.out.print(depthString);
System.out.println("After remove " + val + ": " + res);
ListNode ret;
if (head.val == val) {
ret = res;
} else {
head.next = res;
ret = head;
}
System.out.print(depthString);
System.out.println("Return: " + ret);
return ret;
}
private String generateDepthString(int depth) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < depth; i++) {
res.append("--");
}
return res.toString();
} 控制台输出
点击查看完整内容
1->2->3->5->6->7->8->5->6->NULL Call: remove 6 in 1->2->3->5->6->7->8->5->6->NULL --Call: remove 6 in 2->3->5->6->7->8->5->6->NULL ----Call: remove 6 in 3->5->6->7->8->5->6->NULL ------Call: remove 6 in 5->6->7->8->5->6->NULL --------Call: remove 6 in 6->7->8->5->6->NULL ----------Call: remove 6 in 7->8->5->6->NULL ------------Call: remove 6 in 8->5->6->NULL --------------Call: remove 6 in 5->6->NULL ----------------Call: remove 6 in 6->NULL ------------------Call: remove 6 in null ------------------Return: null----------------After remove 6: null ----------------Return: null --------------After remove 6: null --------------Return: 5->NULL ------------After remove 6: 5->NULL ------------Return: 8->5->NULL ----------After remove 6: 8->5->NULL ----------Return: 7->8->5->NULL --------After remove 6: 7->8->5->NULL --------Return: 7->8->5->NULL ------After remove 6: 7->8->5->NULL ------Return: 5->7->8->5->NULL ----After remove 6: 5->7->8->5->NULL ----Return: 3->5->7->8->5->NULL --After remove 6: 3->5->7->8->5->NULL --Return: 2->3->5->7->8->5->NULL After remove 6: 2->3->5->7->8->5->NULL Return: 1->2->3->5->7->8->5->NULL 1->2->3->5->7->8->5->NULL
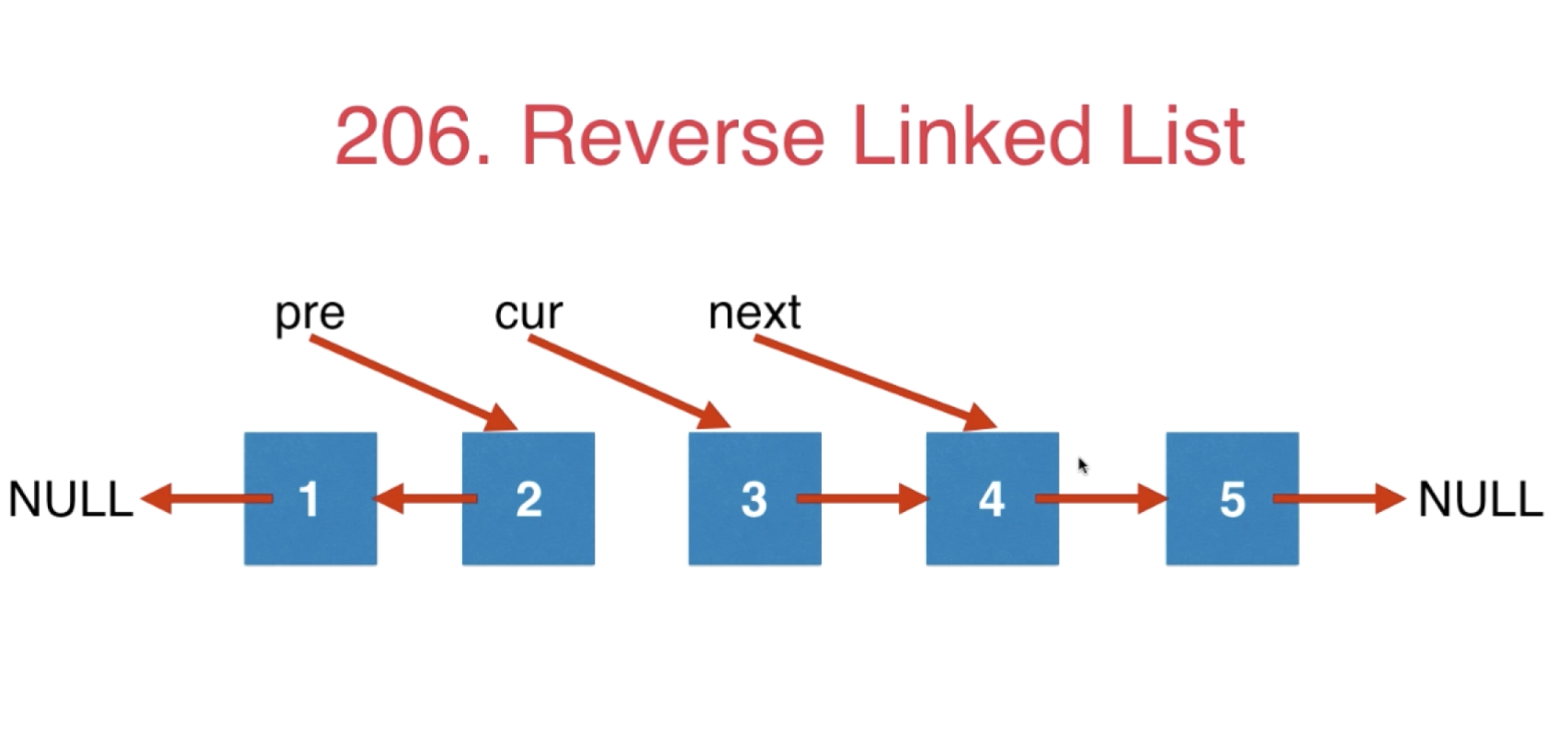
六、链表中最经典的问题,翻转列表
力扣第206题——翻转链表
点我前往题目速览
我们可以定义三个变量来帮助我们实现,如下面这种方式
具体代码如下
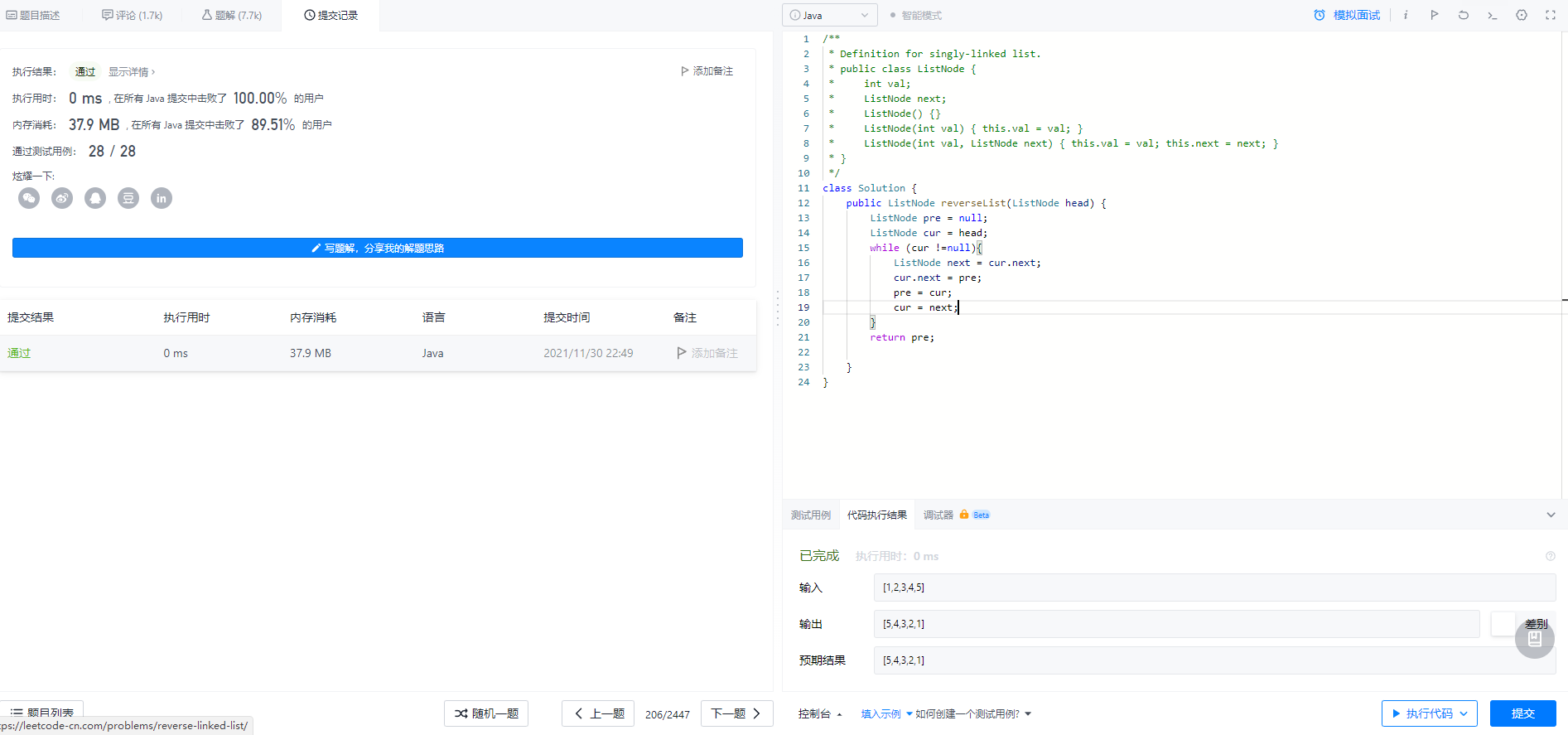
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur !=null){
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
力扣执行结果
七、翻转列表的递归实现
我们先看这串代码
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode rev = reverseList(head.next);
}
}
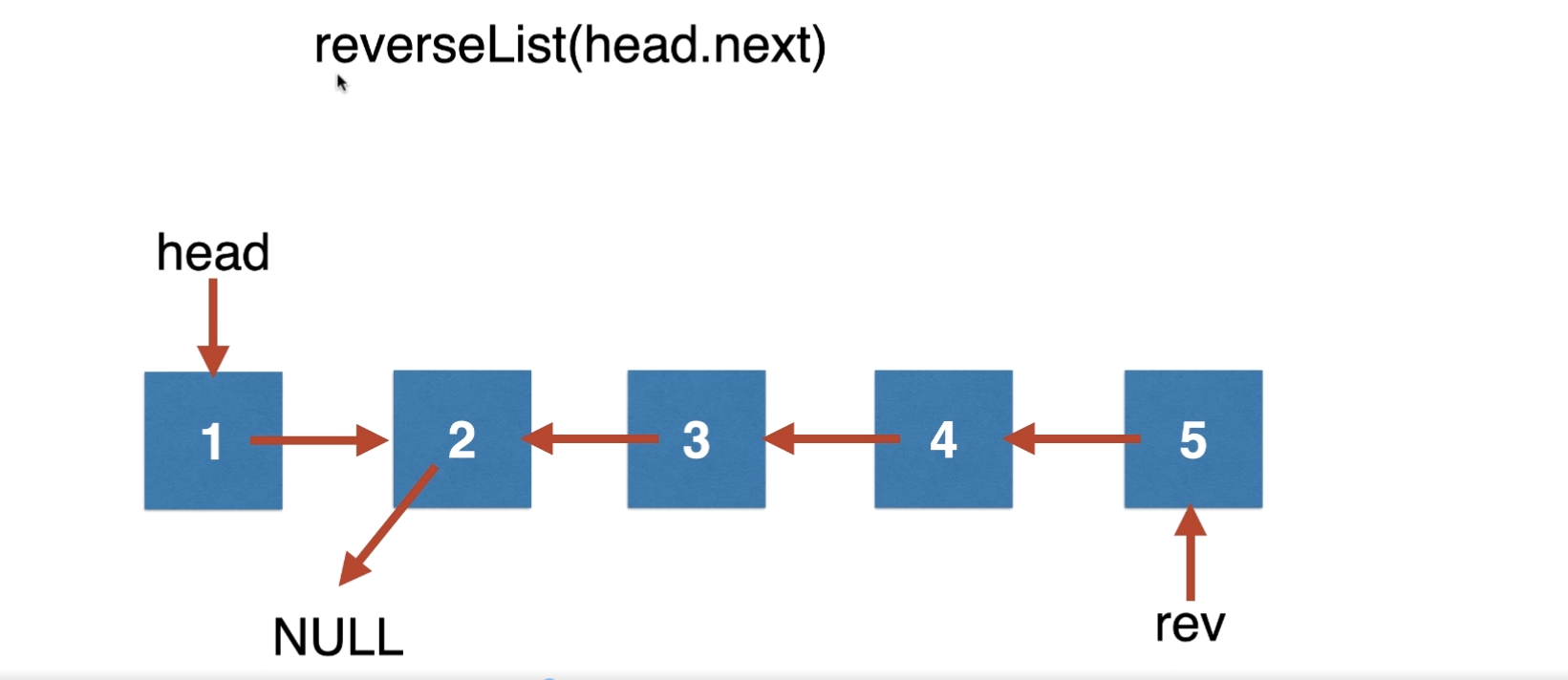
我们从宏观概念上,我们会得到如下链表
完整代码
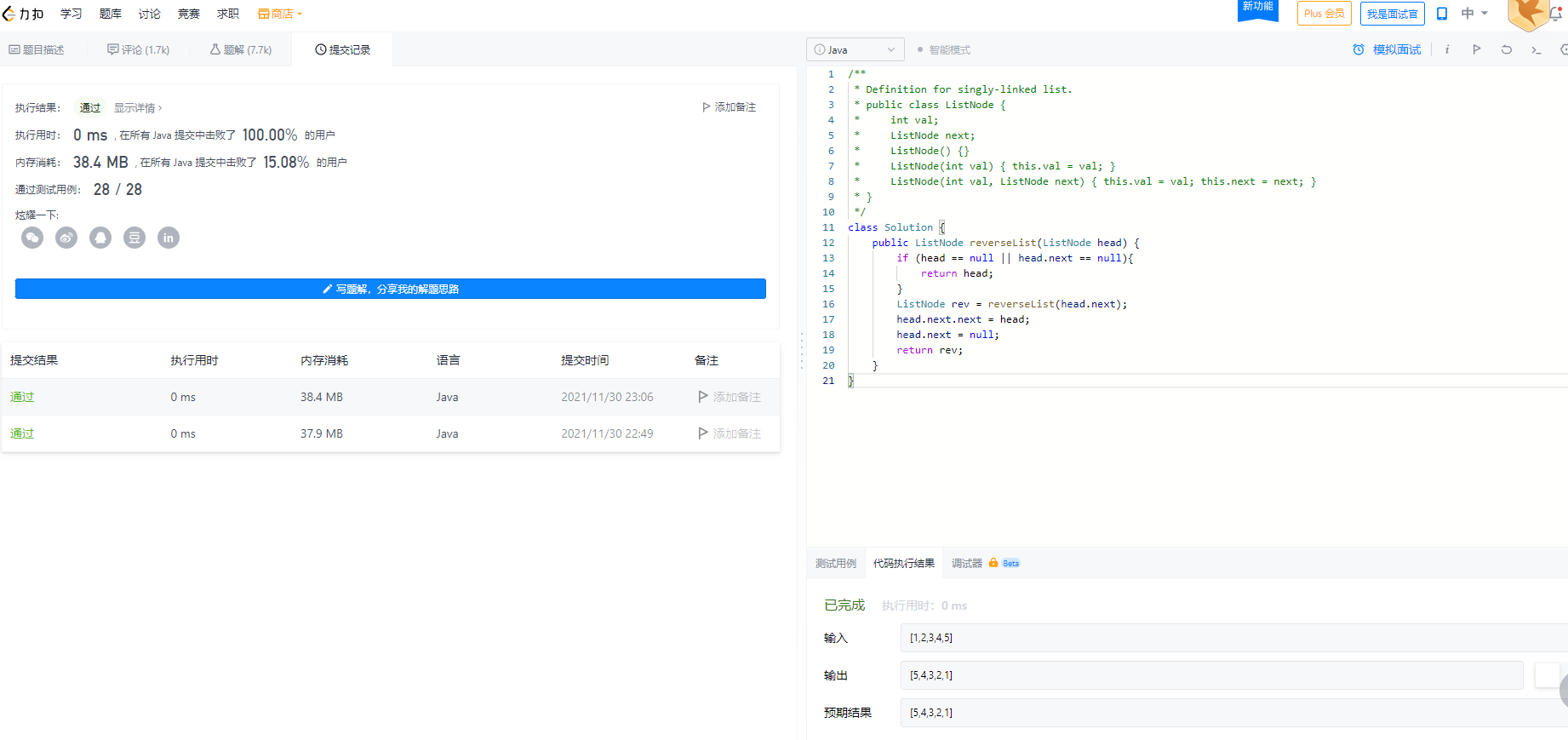
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode rev = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return rev;
}
} 至于为什么输出的是rev,我相信很简单啦,因为我们翻转链表,根据我们的需要,它就是第一个了,从上面的图中也可以清晰的看出来!
力扣输出
本文作者为DBC,转载请注明。